Swollen feet, or edema, occur when excess fluid builds up in the tissues, leading to puffiness, discomfort, or pain.
Occasional swelling after long periods of standing is normal, but persistent or severe cases may signal underlying health issues that need attention.
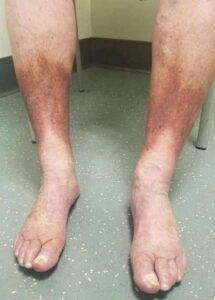
Common Causes
-
Poor Circulation: Conditions like varicose veins or peripheral artery disease can cause blood to pool in the feet.
-
Fluid Retention: High salt intake, hormonal changes, or medications (like steroids or blood pressure drugs) can lead to water buildup.
-
Injury or Inflammation: Sprains, fractures, arthritis, or infections often trigger swelling.
-
Medical Conditions: Heart failure, kidney disease, and liver problems may all cause fluid accumulation.
-
Pregnancy: Increased pressure on blood vessels can lead to mild swelling.
-
Medications: Certain prescriptions, including NSAIDs and hormone therapies, may cause edema.
Symptoms
-
Puffiness or tight shoes
-
Redness, warmth, or tenderness
-
Shiny or discolored skin
-
Reduced mobility
Seek medical help if swelling appears suddenly, affects only one leg, or comes with chest pain, shortness of breath, or fever.
Lifestyle Factors
Prolonged sitting or standing, high-sodium diets, obesity, and inactivity can worsen swelling. Maintaining a healthy weight, moving regularly, and limiting salt intake help prevent it.
Home Remedies
-
Elevate your feet above heart level several times a day.
-
Wear compression socks to improve circulation.
-
Stay active with light exercises and walks.
-
Stay hydrated and reduce salt.
-
Massage or warm baths can also ease discomfort.
Medical Treatment
For chronic or severe cases, doctors may prescribe diuretics, physical therapy, or treatment for underlying conditions such as heart, kidney, or liver disease.
When to See a Doctor
Persistent swelling that doesn’t improve with rest or home care may indicate serious health problems. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications.
Key Takeaway
Swollen feet often reflect more than just fatigue—they can signal circulation or organ issues. Regular monitoring, healthy habits, and timely medical care are essential to maintaining strong, pain-free feet and overall wellness.





