Skin irritation in the groin area is a concern that many people experience at some point in their lives.
The condition can affect both men and women, although certain issues such as fungal infections are more commonly reported in men.
While it may feel uncomfortable or even embarrassing to discuss, groin irritation is a very common problem and is usually treatable with proper care.
Understanding the causes, learning how to identify symptoms, and adopting preventive practices are essential for maintaining skin health in this sensitive area.
This comprehensive guide explores the most frequent causes of groin irritation—including ingrown hairs, folliculitis, fungal infections like jock itch, contact dermatitis, and intertrigo. It also outlines effective strategies for treatment, prevention, and when to seek medical attention. By the end, readers will gain a deeper understanding of why groin skin problems occur and how they can be managed safely.
Why the Groin Area Is Prone to Irritation
The groin is particularly vulnerable to irritation for several reasons:
- Moisture and Sweat: The area tends to retain sweat, especially during hot weather or exercise. This creates an environment where bacteria and fungi can thrive.
- Friction: Skin-to-skin contact, along with rubbing from clothing, can cause chafing and discomfort.
- Hair Removal Practices: Shaving, waxing, or trimming pubic hair can lead to skin trauma, ingrown hairs, or infections.
- Tight Clothing: Restrictive garments reduce airflow, trap moisture, and increase the risk of irritation.
- Sensitivity: The skin in the groin is thinner and more delicate compared to other body areas, making it more reactive to chemicals, allergens, or constant rubbing.
Because of these factors, even small lifestyle changes—such as choice of clothing, hygiene practices, or hair removal methods—can significantly impact skin health.
Ingrown Hairs: A Frequent Culprit
One of the most common issues in the groin area is ingrown hairs. These occur when a hair curls back into the skin rather than growing outward, resulting in small, red, itchy bumps.
Causes:
- Shaving or waxing, especially against the grain of hair growth.
- Wearing tight underwear or pants that press hairs into the skin.
- Having naturally curly or coarse hair, which is more likely to bend back into the skin.
Symptoms:
- Red or dark bumps that may resemble pimples.
- Tenderness, itching, or mild pain.
- Pus-filled lesions if infection develops.
Treatment and Relief:
- Apply a warm compress to soften the skin and encourage the hair to emerge.
- Use gentle exfoliation (such as a mild scrub or washcloth) to remove dead skin cells.
- Avoid shaving or waxing until the area heals.
- Apply over-the-counter creams with soothing ingredients like aloe vera.
- In rare cases of severe infection, a healthcare provider may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics.
Prevention Tips:
- Shave in the direction of hair growth, not against it.
- Use a clean, sharp razor each time.
- Consider alternatives like trimming instead of shaving or waxing.
- Moisturize the area to keep the skin soft and supple.
Folliculitis: Inflammation of Hair Follicles
Another common cause of irritation is folliculitis, which occurs when hair follicles become inflamed due to bacterial or fungal infection, irritation, or blockage.
Causes:
- Tight-fitting clothing that traps sweat.
- Shaving or friction from constant rubbing.
- Swimming in inadequately treated pools or hot tubs.
- Excessive sweating without proper cleansing.
Symptoms:
- Clusters of red or white-headed bumps.
- Itching, burning, or tenderness.
- In more severe cases, swollen painful boils may form.
Treatment:
- Wash gently with antibacterial soap.
- Apply a warm compress to soothe discomfort.
- Use topical antibiotic ointments for bacterial cases.
- In fungal folliculitis, antifungal creams may be required.
- Severe or recurring cases sometimes need oral antibiotics prescribed by a doctor.
Prevention Tips:
- Shower promptly after exercise or swimming.
- Change into dry, breathable clothing quickly.
- Avoid sharing razors or towels.
- Choose looser-fitting clothing made of cotton or moisture-wicking fabrics.
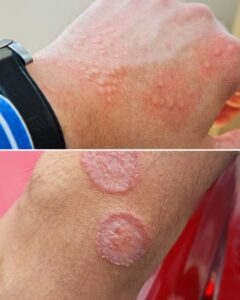
Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris): A Fungal Infection
Tinea cruris, commonly referred to as jock itch, is a fungal infection that affects the groin and upper thigh region. It thrives in warm, damp environments and is especially common among athletes, hence the nickname.
Risk Factors:
- Wearing sweaty clothes for prolonged periods.
- Hot, humid weather conditions.
- Having other fungal infections like athlete’s foot.
- Men are statistically more prone, though women can also develop jock itch.
Symptoms:
- Red, itchy, scaly patches that may spread outward while clearing in the center.
- Burning or stinging sensations.
- Discomfort that worsens with sweating or physical activity.
Treatment:
- Apply over-the-counter antifungal creams, powders, or sprays.
- Keep the groin clean and dry.
- Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing.
- In persistent or severe cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger antifungal medication.
Prevention Tips:
- Change underwear daily.
- Avoid sharing towels or athletic gear.
- Dry the groin thoroughly after bathing or swimming.
- Use antifungal powders if prone to recurrent infections.
Contact Dermatitis: Allergic and Irritant Reactions





